- Weight: is combat loaded, Speed: maximum road, Range: on road with internal consumption (cross country is approximately 2/3 of this figure), Armor: thickness in mm front/side/rear.

Type: Hotchkiss H-39
Weight: 12 tons
Speed: 23 mph
Range: 100 miles
Armament: 37mm SA 38, 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 40/30/20
The H-35 was the earlier version of this Hotchkiss tank. Fifteen of these, returning from Norway, were left in England to become the nucleus of Free French Armour.
Type: Renault R-35
Weight: 12 tons
Speed: 12 mph
Range: 120 miles
Armament: 37mm SA 18, 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 40/30/20
Crew: 2
R-35 battalions made up one-third of the available French armoured units in 1940. These tanks were cramped and badly sprung, giving a bad ride.
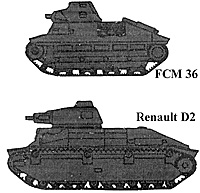
Type: FCM 36
Weight: 13 tons
Speed: 15 mph
Range: 120 miles
Armament: 37mm SA 18, 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 40/30/20
Crew: 2
The FCM came into service in 1937. It was a mediocre tank along the lines of the
Renault 35. Only two battalions were formed with this tank.
Typa Renault D2
Weight: 22 tons
Speed: 15 mph
Range: 140 miles
Armament: 47mm SA 35, 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 40/30/20
Crew: 3

Type: Somua S-35
Weight: 22 tons
Speed: 25 mph
Range: 100 mi les
Armament: 47mm SA 35, 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 40/30/20
Crew: 3
The best French tank was a cavalry vehicle in the DLMs. The Somua had comparable speed and a superior gun and armour to German tanks. Its only drawback was the small crew.
Type: Renault B1 bis
Weight: 32 tons
Speed: 18 mph
Range: 140 miles
Armament: 75mm, 47mm SA 35, 2 - 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 60/40/20
Crew: 4
Introduced in 1936, the char B became the main battle tank of the Division Cuirassee. Its thick armour made it immune to all but the German 75mm and 88mm guns.
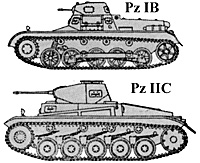
Type: Pz Kpfw I B
Weight: 5.7 tons
Speed: 25 mph
Range: 95 miles
Armament: 2 - 7.92mm MG 34
Armor: 15/15/15
Crew: 2
Type: Pz Kpfw II C
Weight: 8.6 tons
Speed: 25 mph
Range: 125 miles
Armament: 20mm KwK 30 or 38 L/55, 7.92mm MG 34
Armor: 15/15/15
More like fully-tracked armoured cars than tanks, the Panzer I and II were originally intended for use only as training and reconnaissance vehicles. The failure of German production to build adequate numbers of newer heavier tanks necessitated keeping these two models as the main armament with the Panzer Division.
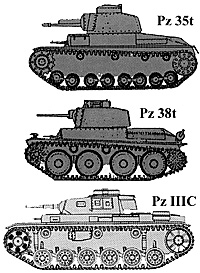
Type: Pz Kpfw 35t
Weight: 11 tons
Speed: 22.5 mph
Range: 125 miles
Armament: 37.2mm L/40 A3, 2 -- CZ
Type: 37 7.92mm MG
Armor: 25/16/16
Crew: 4
Type: Pz Kpfw 38t
Weight: 10 tons
Speed: 26.5 mph
Range: 125 miles
Armament: 37.2mm L/47.8 A7, 2 -- CZ
Type: 37 7.92mm MC
Armor: 25/16/16
Crew: 4
When Germany took over Czechoslovakia in 1938, all of the Czech army s equipment came into the Wehrmacht, including 469 modern tanks. These two
Type: s formed three new Panzer Divisions after the Polish Campaign.
Type: Pz Kpfw III C
Weight: 18 tons
Speed: 25 mph
Range: 105 miles
Armament: 37mm KwK 35 L/45, 2 - 7.92mm MG 34
Armor: 30/30/20
Crew: 5
Panzer III Production was almost 200 tanks short of what the establishment for the Panzer Divisions required. It was meant to be the standard tank of the light companies, but Panzer IIs had to be substituted in many cases.
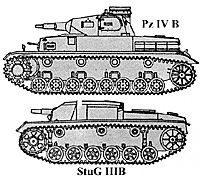
Type: Pz Kpfw IV B
Weight: 19 5 tons
Speed: 25 mph
Range: 125 miles
Armament: 75mm KwK 37 L/24, 7.92mm MG 34
Armor: 30/30/20 9
Crew: 5
Germany's best tank, the Panzer IV, was supposed to provide fire support for the lighter tanks. However, it often had to call for fire support itself, as its low-velocity gun could not penetrate the average French armor at over 250 yards range.
Type: StuG III B
Weight: 20.2 tons
Speed: 25 mph
Range: 102 miles
Armament: 75mm StuK 37 L/24, 2 - 9mm MP
Armor: 50/30/30
Crow 4
Six StuG III assault guns were tested in the field with the Gross Deutschland Motorized Infantry Regiment. This successful experiment led to extensive development of armoured infantry support guns.

Type: Light Tank Mk VI B
Weight: 5 tons
Speed: 35 mph
Range: 130 miles
Armament: .5" and .303" Vickers
Armor: 14/12/4
Crew: 3
The Mk VI was first introduced in 1938, and was basically the equivalent of the German Panzer I. Some vehicles had the Besa 15mm and 7.92mrn MG in place of the Vickers water-cooled
Type: s.
Type: Renault FT-17
Weight: 7 tons
Speed: 5 mph
Range: 24 miles
Armamant 37mm SA 18 or 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 22/15/6
Crew: 2
The FT-17 was a WWI veteran that remained France's main tank up to the mid thirties.
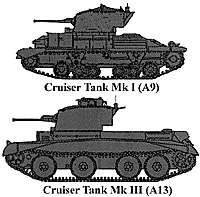
Type: Cruiser Tank Mk I (A9)
Weight: 12 tons
Speed: 25 mph
Range: 100 miles
Armament: OQF 2 par, 3 - .303" Vickers MG
Armor: 14/14/6
Crew: 4
Type: Cruiser Tank Mk III (A13)
Weight: 14 tons
Speed: 30 mph
Range: 90 miles
Armament: OQF 2 par, .303" Vickers MG
Armor: 30/30/20
Crew: 4
The Cruiser series was supposed to fulfill Britain's armour enthusiasts' idea of a mobile tank able to penetrate deep behind enemy lines. The A9 was chosen in 1937 as a stop-gap to meet this demand. The A10 which followed was more heavily armored and consequently slower. It was the A13. a very mechanically reliable tank, that had the greatest potential in 1940 as a cruiser.

Type: Infantry Tank Mk I (All)
Weight: 11 tons
Speed: 8 mph
Range: 80 miles
Armament: .5" or.303" Vickers
Armor: 60/60/20
Crew: 2
Type: Infantry Tank Mk II (A12)
Weight: 26.5 tons
Speed: 15 mph
Range: 60 miles
Armament: OQF 2 par, .303" Vickers MG
Armor: 78/65/20
Crew: 4
The demand for infantry support competed with the cruiser tank theory, resulting in the slow, heavily armoured A11 and A12. Designed under the code "Matilda", this name was eventually given to the Mk II infantry tank. The Mk I performed quite well when used in the counter-attack at Arras on May 21. The Mk II close-support tank had a 3" howitzer in place of the 2 pounder gun.
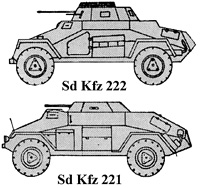
Type: Sd Kfz 221 & 222
Weight: 4 tons
Speed: 46 mph
Range: 175 miles
Armament: 20mm KwK 30 or 38, 7.92mm MG 34
Armor: 14/8/8
Crew: 2-3
These four-wheeled vehicles were the most widely used German light armoured cars in World War II. They formed the bulk of the reconnaissance units in panzer and motorized infantry divisions.
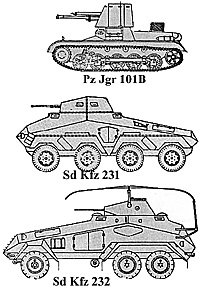
Type: Sd Kfz 231
Weight: 8.3 tons ip,
Speed: 53 mph
Range: 186 miles
Armament: 20mm KwK 30 or 38 L/55, 7.92mm MG 34
Armor: 14/8/8
Crew: 4
Type: Pz Jgr Sd Kfz 101 B
Weight: 6.5 tons
Speed: 24.5 mph
Range: 95 miles
Armament: 47mm Pak (t} L/43, 9mm MP
Armor: 13/13/13
Crew: 3
Type: Sd Kfz 232
Weight: 5.9 tons
Speed: 37mph
Range: 155 miles
Armament: 20mm KwK 30 L/55, 7.92mm
Armor: 14/8/8
Crew: 4
The Sd Kfz 231 was just coming into service at the start of tne 1940 campaign. It was the heavy reconnaissance car for the motorized forces when in close contact with the enemy. This armoured car gave very poor cross-country performance and was meant to be an interim vehicle, to be used until the new eight-wheeled cars could replace it.
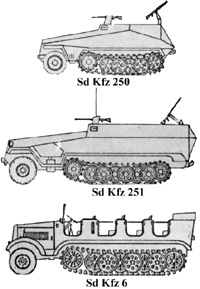
Type: Sd Kfz 250
Weight: 5.7 tons
Speed: 37.5 mph
Range: 200 miles
Armament:
Armor: 14/8/8
Crew: 6
Type: Sd Kfz 251
Weight: 8.5 tons
Speed: 32 mph
Range: 112 miles
Armament: --
Armor: 14/8/8
Type: Sd Kfz 6
Weight: 9.7 tons
Speed: 30/12 mph
Range: 186 miles
Armament: --
Armor: 14/8/8
Crew: 12; tow 2.7 tons
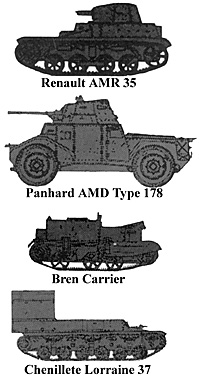
Type: Renault AMR 35
Weight: 5 tons
Speed: 30 mph
Range: 120 miles
Armament: 13.2mm or 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 15/15/15
Crew: 2
Very similar to Germany's Panzer I, the AMR 35 was an integral part of the dragons portes. This fully-tracked armoured car had an excellent cross country performance.
Type: Panhard AMD
Type: 178
Weight: 8.5 tons
Speed: 45 mph
Range: 185 miles
Armament: 25mm L/73, 7.5mm MG 31
Armor: 20/15/15
Crew: 4
The Panhard 178 was the finest vehicle of its
Type: in the 1940 campaign. This four- wheel drive car equipped the infantry and cavalry reconnaissance units.
Type: Bren Universal Carrier
Weight: 4 tons
Speed: 30 mph
Range: 130 miles
Armament: Boys .55" AT rifle, Bren LMG
Armour 10/7/7
Crew: 3(+3- 5)
Peculiar to British and Commonwealth armies, the open carrier was mostly of the universal
Type: , although it's best known as Bren. It carried infantry and mounted various weapons, acting both as transport and AFV.
Type: Chenillette Lorraine 37
Weight: 6 tons
Speed: 22 mph
Range: 85 miles
Armament: (none)
Armor: 6/6/6
The Chenillette Lorraine was used both as a supply vehicle and a troop transport in France's armoured divisions. Conceived in 1935, ammunition and refueling vehicles began entering service in 1937. The first deliveries of the APC version (shown here) did not take place until 1940.
More 1940
-
1940: Campaign in France
1940: Campaign in France: Military Dictionary
1940: Campaign in France: TO&E: French
1940: Campaign in France: TO&E: British
1940: Campaign in France: TO&E: German
1940: Campaign in France: Tank Illustrations and Specs
1940: Campaign in France: Anti-Tank Gun Comparison
1940: Campaign in France: Order of Battle Numerical Charts
Related
Back to Conflict Number 1 Table of Contents
Back to Conflict List of Issues
Back to MagWeb Master Magazine List
© Copyright 1998 by Dana Lombardy
This article appears in MagWeb (Magazine Web) on the Internet World Wide Web.
Other military history articles and gaming articles are available at http://www.magweb.com