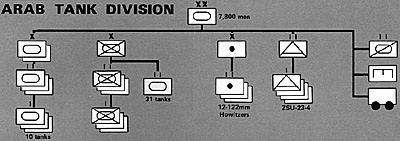
Arab Tank Division
On paper the Egyptian armored division (250 tanks, 150 APC's) was a more balanced force at the start of the October War (Ramadan War to the Arabs) when compared to 1973 Israeli tank units. Following the Soviet model, several changes were made for the Middle East. The mechanized infantry brigade (called a "regiment " in Russian formations) included a battalion of tanks, while anti-tank (AT) weapons were liberally distributed among the infantry: Sagger AT missiles at brigade-level; recoilless rifles at battalion-level; and RPG- 7 (rocket propelled grenade) at platoon level. Whereas the Jewish tank units were to be committed immediately at the start of hostilities, the Egyptian armored divisions (two had been organized for the War) true to Soviet doctrine were not to become engaged until several days after the bridgeheads on the east bank were established.
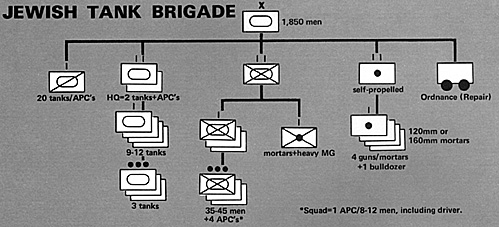
Jewish Tank Brigade
In both the Six-Day and Yom Kippur Wars the basic unit of the I.D.F. was the brigade (CHATIVAH). In the 1967 War the Jews had time to organize and deploy their forces according to a set plan. Most tank brigades therefore appeared as shown above. 2-3 brigades were grouped together under an UGDAH (literally "taskforce") and this divisional structure had become standardized by the 1973 War. Each of these UGDAHS or Tank Divisions had its own reconnaissance unit, nine self-propelled artillery batteries (155mm guns or 160mm mortars), as well as engineer, ordnance (repair), and antiaircraft units. The Jews did not have time to bring all of their formations to battle in 1973 as complete units.Platoons (MACHLAKAH), companies (PLUGAH), and battalions(GDUD) were fed piecemeal to thefronts, formed into ad hoc units or distributed among the brigades already there. Adding to this general disorganization was the neg/ect of the armored infantry between the wars. While most mechanized infantry units' M.3 halftracks had been replaced with newer U.S. M. 113 APC's, in 1973 many tank brigades had 2-3 tank battalions only and no infantry component. (Somen'meS even the brigade artillery battalion was missing) This all-armor doctrine still succeeded in stopping the Arabs on both fronts, but at a cost of hundreds of tanks lost to Arab infantry A T weapons. To rectify this, by the second week of the October War a mechanized infantry company was assigned to each tank battalion (replacing the 4th tank company). Even this proved insufficient and more infantry (including paratroops) were attached to the brigades.
More Arab-Israeli Armor 1973
-
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Introduction
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: T-54/55/62
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: M-48/60
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Centurion Mk 5
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: TO&E
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Jewish Tank Markings
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Tanker Crew
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Comparative Data (Chart)
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Comparative Ammunition
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Observations and Conclusions
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Paper Tanks
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Bibliography
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: Glossary of Terminology
Arab-Israeli Armor 1973: 1/64 Scale Illustrations (extremely slow: 439K)
Back to Table of Contents -- Conflict Special Study 1
Back to Conflict List of Issues
Back to MagWeb Master Magazine List
© Copyright 1975 by Dana Lombardy.
This article appears in MagWeb (Magazine Web) on the Internet World Wide Web. Other military history articles and gaming articles are available at http://www.magweb.com