 The first requirement for a good referee in Brigade Series games
(after knowing the rules) is to have a fine grasp of line-of-sight.
Nothing will make a player more frustrated than feeling that you are
not telling him everything he can see. However, if you are telling him
more than he can see, you ruin the verisimilitude. In our recent playing
of Barren Victory , there was no visibility in all that wooded
Chickamauga bottom land. I spent most of my time telling players what
they were hearing, since usually they were seeing nothing but trees. Now
I am refereeing a game of Thunder at the Crossroads , with its wide,
deep fields of vision, and line-of-sight is a major job. I must tell each
player what he saw during friendly movement, friendly combat
(including retreats), enemy movement, and enemy combat (including
retreats). If my line-of-sight chops are not up, the game is down the
tubes.
The first requirement for a good referee in Brigade Series games
(after knowing the rules) is to have a fine grasp of line-of-sight.
Nothing will make a player more frustrated than feeling that you are
not telling him everything he can see. However, if you are telling him
more than he can see, you ruin the verisimilitude. In our recent playing
of Barren Victory , there was no visibility in all that wooded
Chickamauga bottom land. I spent most of my time telling players what
they were hearing, since usually they were seeing nothing but trees. Now
I am refereeing a game of Thunder at the Crossroads , with its wide,
deep fields of vision, and line-of-sight is a major job. I must tell each
player what he saw during friendly movement, friendly combat
(including retreats), enemy movement, and enemy combat (including
retreats). If my line-of-sight chops are not up, the game is down the
tubes.
However, the subject of line-of-sight is so slippery that I have not found an exhaustive treatment of it in any game I have ever owned. For instance, here is how the estimable Richard Berg weighs in on the subject in recent GBACW rules: "LOS involves making three-dimensional decisions from a two-dimensional source. It can be confusing. The basic rule is common sense, followed by extensive coin-flipping." So far as Mr. Berg is concerned, you are on your own and good luck.
I find The Gamers' rules have made the best attempts at nailing down the elusive LOS algorithm, but even their most recent formulations, in the CWB 2nd Ed. and the NBS, lose focus at different points. I have tried to combine the strengths of The Gamers' two methods and eliminate the weak spots.
Algorithm for Line-of-Sight
A. Each hex has a terrain (elevation) level. From lowest to highest, the terrain levels are I through 8.
B. Forest, Orchard, and Town hexes add one to the terrain level of their hex when determining blockage of the Line of Sight (LOS). Combat units and wagons add 1/4 to the terrain level of their hex. We will call these features modifiers.
C. With any modifiers means that you include any modifiers in the hex when determining the terrain level of the hex. Without modifiers means that you do not include any modifiers in the hex when determining the terrain level of the hex. Always consider the sighting hex A and the target hex B as without modifiers.
D. LOS between adjacent hexes is never blocked.
Sighting Procedure
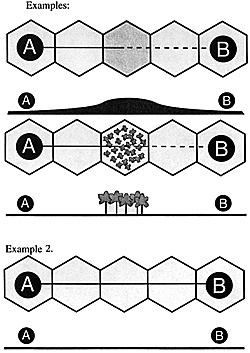 Draw a line from the center of the sighting hex to the
center of the sighted hex. This is the LOS, or line-of-sight. Only
terrain levels and modifiers intersected by this line may block LOS.
(Exception: see Special case #1 below.)
Draw a line from the center of the sighting hex to the
center of the sighted hex. This is the LOS, or line-of-sight. Only
terrain levels and modifiers intersected by this line may block LOS.
(Exception: see Special case #1 below.)
Compare the terrain levels in the sighting hex A, the target hex B, and the intervening terrain according to the following propositions.
1. No terrain (with any modifiers) higher than both A and B exists between them.
True-Go to the next line.
False-LOS is blocked. (Terrain higher than both the sighting and sighted hexes always blocks LOS.)
Examples:
2. A and B have the same terrain level.
True-LOS is not blocked. (With no obstruction between them--determined by line 1--units on the same level can always see each other.)
False-Goto the next line. (A and Bare on different terrain levels.)
Example:
3. Terrain (with any modifiers) exists between A and B that is the same level as the higher of the two.
True-Go to the next line.
False-Go to line 7.
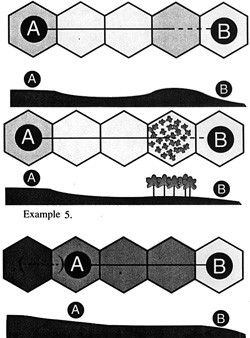 4. This terrain (with any modifiers), the same level as
the higher of the two, is separated from the higher of the two by
lower terrain (without modifiers) at any point between them.
4. This terrain (with any modifiers), the same level as
the higher of the two, is separated from the higher of the two by
lower terrain (without modifiers) at any point between them.
True-LOS is blocked.
False-Go to the next line.
(Together with steps 2 and 3, this line determines if the LOS is obstructed by an intervening ridge.)
Examples :
5. The LOS, if extended past the higher of the two (that is away from the lower of the two), crosses higher terrain (without modifiers) before crossing lower terrain (without modifiers).
True-Go to line 7. (If this is true, the sighting A and the sighted B are both on the same side of a hill crest.)
False-Go to the next line.
Example:
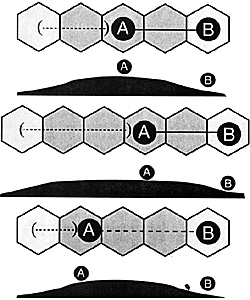 6. The distance past the higher of the two (that is,
away from the lower of the two) to lower terrain (without modifiers)
is greater than or equal to the distance from the higher of the two to
lower terrain (without modifiers) in the direction of the lower of the
two.
6. The distance past the higher of the two (that is,
away from the lower of the two) to lower terrain (without modifiers)
is greater than or equal to the distance from the higher of the two to
lower terrain (without modifiers) in the direction of the lower of the
two.
True-Go to the next line. (A and B are both on the same side of a hill crest.)
False-LOS is blocked. (They are on opposite sides of a hill crest.)
Examples:
7. No terrain between A and B has modifiers.
True-Go to the next line.
False-Go to line 11, using all intervening hexes with modifiers as Contention hexes.
Example: see line 11
8. The difference in elevation between A and B is 1 level.
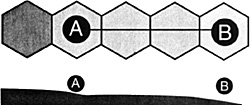 True-LOS is not blocked. (With no terrain higher than
both between them--determined by line 1, no intervening ridgesline 4,
on the same side of a hill crest-lines 5 and 6, and no obstructing
modifiers--line 7, units with I level difference have only a gradual
slope between them and can always see each other.)
True-LOS is not blocked. (With no terrain higher than
both between them--determined by line 1, no intervening ridgesline 4,
on the same side of a hill crest-lines 5 and 6, and no obstructing
modifiers--line 7, units with I level difference have only a gradual
slope between them and can always see each other.)
False-Go to line 9. (There is more than I terrain level difference between A and B.)
Example:
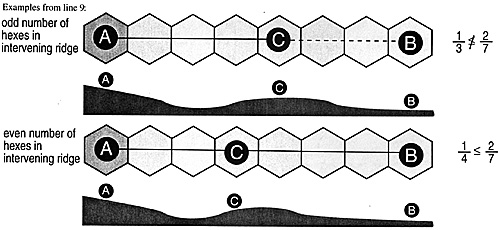 9. There is intermediate level terrain (with any
modifiers) between A and B that is separated from the higher of the
two by lower terrain (without modifiers) at any point between them.
9. There is intermediate level terrain (with any
modifiers) between A and B that is separated from the higher of the
two by lower terrain (without modifiers) at any point between them.
True-Go to line 11, using the middle hex (moving along the LOS from higher to lower) of the intermediate level terrain described above as the Contention hex. (if this is true, there is an intervening ridge of intermediate-level terrain between A and B. YOU must check that ridge-at its crest/middle if it is more than I hex across-in step 11 to see if it is high enough to block LOS.)
False-Go to the next line.
Example: see line 11
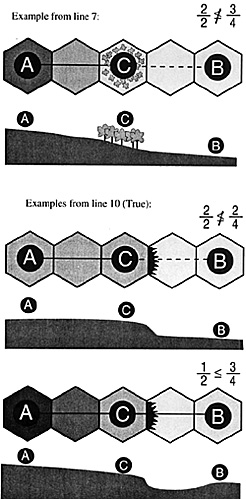 10. LOS between A and B crosses (not runs straight
along) a Slope or Extreme Slope hexside. (For LOS that runs along a
Slope or Extreme Slope hexside, see Special case #1 below.)
10. LOS between A and B crosses (not runs straight
along) a Slope or Extreme Slope hexside. (For LOS that runs along a
Slope or Extreme Slope hexside, see Special case #1 below.)
True-Go to the next line, using the higher of the two hexes adjacent to the Slope or Extreme Slope hexside as the Contention hex.
False (That is, the difference in elevation between A and B is more than I level, but LOS does not cross Slope or Extreme Slope hexsides)-Go to the next line, using thefirst hex (moving along the LOS from higher to lower) of all intermediate terrain levels as Contention hexes.
(if this is true, there is a sudden drop-off in the terrain, rather than a gradual slope, and hexes may be hidden from view, sheltered by the steep slope. If it is false, there is still a chance that the gradual slope of the terrain may get steep enough to obstruct view into some hexes.)
Example: see line 11
11. There is no hex (call it the Contention hex) such that its terrain level (with any modifiers) minus the terrain level of the lower of the two (call it B), divided by the distance in hexes from the Contention hex to B, is greater than the terrain level of the higher of the two (A) minus the terrain level of the lower of the two (B), divided by the distance in hexes from A to B.
That is:
- (hC-hL)/dCL is less than or equal to
(hH-hL)/dHl
Where:
- hC: Height of Contention
hL: Height of Lower
hH: Height of Higher
dCL: Distance from Contention to Lower
dHL: Distance from Higher to Lower
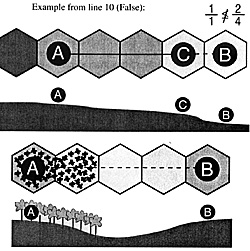 True-LOS is not blocked
True-LOS is not blocked
False-LOS is blocked. (This formula will determine whether the intervening terrain considered in lines 7, 9 and 10 is high enough to block LOS.)
Special case # 1: A hexside does not block a LOS that runs straight along it if the unit could see through one of the two hexes next to the hexside.
Special case #2: You may not trace LOS into or out of a Forest, Orchard, orTown hex through an adjacent Forest, Orchard,or Town hex that is I level lower. (This special case simulates a continuous obstructing canopy that follows the gradual slope of the terrain.)
Example:
Back to Table of Contents -- Operations #15
Back to Operations List of Issues
Back to MagWeb Master List of Magazines
© Copyright 1994 by The Gamers.
This article appears in MagWeb (Magazine Web) on the Internet World Wide Web.
Other military history articles and gaming articles are available at http://www.magweb.com