Belgium
This country has announced that it will be going over to a single service structure and that it will specialize in humanitarian activities with only residual warfighting capability.
Egypt
The US is selling Egypt 53 RGM-84L Harpoon II missiles and four Phalanx gun systems for the US-built Ambassador III-class patrol boats. The Israelis were not pleased with the proposed Harpoon II sale until the US promised to modify the software so that the missile’s land-attack capability is removed.
Statistics for the Ambassador III class:
- Ambassador III PTG
Displacement: 550 std
In class: 0+0+4
Acoustic Counterm: NoneBR> In Service: 2005
Electronic Counterm: 3rd Gen J&DBR> ESM: 3rd Gen
Propulsion: Diesel BR>Crew: 36
Size Class: Small BR>Signature: VSmall/Noisy
Weapons: ROF
F(1)1 Mk75 76mm/62//EO director C/USA
A(21)1 Mk49 w/21 RIM-116A RAM (15) D/Intl
A(R)1 Mk15 Phalanx Blk IB 20mm w/7 bursts C/USA
PB&SB(4)2 Mk141 w/4 RGM-84L Harpoon II (8) D/USA
Sensors: TRS-3D J/FRG
Scout nav radar J/Nethl.
Remarks:
Built in the US. Will be delivered one per year starting 2005. Reduced signature. Mk75 gun upgraded. Use stats for Italian
Super Rapid 76mm/62. Endurance 8 days.
Damage and Speed Breakdown:
Dam Pts: 0 71420 24 27
Surf Speed: 41 31 21 11 0 Sinks
The first unit will be commissioned in 2005, with one more being delivered each year.
The only potential problem is the shipbuilder. The original vendor, Halter, is in bankruptcy (it wasn’t when the deal was made), and so the Egyptians may have to find another builder. It has to be a U.S. shipyard, since U.S. funds are paying for the boats.
France
Eight new multi-mission frigates of an eventual class of 17 have been announced. These ships will be equipped with PAAMS and a VLS-launched version of SCALP/Storm Shadow.
Six Barracuda-class SSNs have also been announced but there is no mention of a second nuclear-powered aircraft carrier to supplement the unlucky Charles de Gaulle.
India
While the “Will they/Won’t they” debate continues over Gorshkov, more obvious signs of Indo-Russian cooperation have been taking place. The recent test firing in India of the 3M55/ Yakhont [SS-NX-26] missile have been followed up by the announcement that it will enter Indian service in 2003 as the PJ-10 Brahmos with surface-, sub- and air-launched variants. There are ten Russian-built Kilo subs in Indian service. A fourth Indian Kilo has completed its refit in Russia, which means that, counting one sub built with the capability, half the force has the ability to fire the Klub family of missiles including the 3M54E (Novator Alfa).
Israel
A new active homing air-to-air missile, Derby, was unveiled last Summer at the Paris Air Show. This 3.62 m-long missile can achieve sustained turn rates of 60 – 70g and has a range of 35 nm. The missile uses a derivation of the Python 4 motor and warhead with a new radar seeker in the same class as AMRAAM. While not in use by the Israeli Air Force (we think), Rafael, the manufacturer, claims to have sold it to several countries.
Derby is actually the export name. It may be called “Alto” by the Israeli Air Force. Derby can be carried on a Python 4 launcher, which makes it attractive to any customer already using the Python (like China). India also expressed interest in Derby, but has not announced any purchase.
For Harpoon, treat it as a 4th Gen I/TARH missile with ATA ratings of 6.0/7.0 (like all TARH AAMs, it is capable of boresight launch, which is when the second value is used). It weighs 118 kg. Its speed and ceiling are probably similar to the Python at 1721 kts and 18000 m. It can be used with helmet-mounted sights (HMS) and displays (HMD). Israeli helmet-mounted display-equipped F-16s scored 220:20 kills against non-HMS equipped USN F/A-18s in recent exercises.
 Italy
Italy
The new aircraft carrier, Andrea Doria, will enter service in 2008. Formerly called the NUM (“new major vessel”), this 235 m-long, 22,500-ton ship will carry a mix of AV-8B+ and EH.101 aircraft. It is also capable of carrying 450 troops.
Italian Navy AV-8Bs have been certified to carry AMRAAM as of March 2002.
Latvia & Lithuania
These countries each got three Storm class FACs from Norway last year. One of each group are intended to provide spares to their sisters. Whilst the TVT300 optical sights have been retained, all other military sensors and fire control have been removed before delivery. They will keep the 40mm and low-angle 76mm/50 guns.
Netherlands
The Dutch F-16 Mid Life Update (MLU) has been announced. The capability enhancements include Night Vision Goggles (NVG), the US LANTIRN system and the ability to launch AMRAAM, Paveway III, and AGM-65G Maverick. The ability to fire GPS-guided weapons will be provided from 2003.
A second LPD, Johan de Witt, was ordered 4 April 2002. This vessel will come with extensive command and control capabilities.
The three remaining Kortenaer-class frigates will leave service by 2004.
Poland
This country is acquiring its second FFG-7 and 4 SH-2G to operate from them.
The three Orkan-class corvettes are being fitted with RBS15 missiles. Poland is also in the market for ex-Norwegian equipment, having acquired four Kobben-class submarines, which will enter service in 2003 carrying Swedish Type 61 torpedoes. The first has already been delivered. A fifth unit, Kobben herself, will be transferred in August or September as a source of spares.
In order to achieve their goal of having NATO-compatible aircraft, the Polish MiG-29 fleet is being modified, and they will be joined by 22 similar aircraft, currently operated by the German Luftwaffe.
Longer-term plans include seven MEKO 100 class corvettes, of which two will be in service by 2006. In 2004, the remaining MiG-21s, two Foxtrot subs, and Warszawa (mod Kashin) will be deleted.
 Russia
Russia
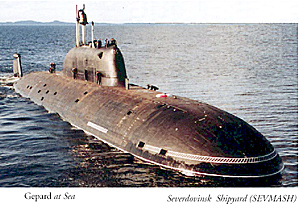
K-335 Gepard, a Project 971M Shchuka-Bars [Akula II] nuclear submarine, joined the Northern fleet on 4 December 2001. Gepard means “Cheetah” in Russian.
This is news only because it is the first new Russian sub commissioned in six years, and only after a protracted construction. Laid down in September of 1991, she was originally scheduled to be finished in 1996.
President Putin also attended her launch in 1999. His presence at her commissioning showed his support for a navy battered by the loss of Kursk, built at the same shipyard, and Putin’s purge of the Northern Fleet staff. These dismissals and demotions happened just days before Gepard’s commissioning ceremony.
Two other submarines, a new SSN named Severdovinsk (keel laid Nov 93) and a new SSBN named Yuri Dolgoruiky (keel laid Nov 96), are also under construction at the same shipyard, but have suffered similar extended delays. There is no information on when, if ever, they will be completed.
A new corvette design was laid down in the St. Petersburg yard on 21 Dec 2001. Stereguschyii, which means “On Guard,” displaces 2200 tons and has a reduced radar signature. It is described by the Russians as “using stealth technology.” Construction is expected to be complete by 2004-05.
Spain
SH-60Bs going to Spain are to be fitted with FLIR and capable of launching the B and K versions of the Hellfire missile. The Spanish Navy AV-8Bs have been certified to carry AMRAAM as of March 2002.
Sweden
Details of the unique Swedish datalink system fitted in Viggen and Gripen have been disclosed. Up to four aircraft can use the system together, which enables one aircraft to fire missiles tracked by other aircraft. If three or more aircraft are tracking the target, sufficient information is available to enable missile lock on without direct illumination of the target (ESM will detect the multiple paints but RWR will not react). The system is claimed to be jam-proof and also offers the ability of one radar in the flight to jam detecting ESM systems to prevent detection of other radars from the flight.
This year the Swedish Air Force will be downsized to a total of 8 Gripen squadrons and one C-130 squadron.
Taiwan
The US government has offered Taiwan the four Kidd-class destroyers, twelve P-3 Orions, Harpoon SSMs and Mk48 Mod 4 torpedoes.
A Taiwanese delegation arrived in the US in May to negotiate the actual price. While the sale appears firm, they are trying to dicker down the cost of the ships (before modernization). A Swedish admiral, the head of their submarine service, has written an article about the usefulness of submarines rines in the defense of Taiwan. He states that the shallow water in the area could be used effectively by submarines, and that the AIP systems used by Swedish subs would be an excellent feature for any Taiwanese sub.
Sweden’s submarine industry already has a presence in Asia. They’re involved in sub programs in Australia and Malaysia. HDW, the German submarine builder, has also shown interest, but has bought Kockums, the Swedish sub company. HDW in turn is owned by an American investment firm, and President Bush supports the idea of Taiwan receiving modern subs.
United Kingdom
As part of the transition to a single fleet of aircraft, the remaining 24 Sea Harrier FA.2s are all being retired and replaced in active duty with a fleet of 35 Harrier GR.7s, which do not have a radar or radar AAM capability. According to the current plan, they will be phased out between 2004 and 2006. The announcement was made in February of this year.
Although the Sea Harrier was not a stellar air defense aircraft, it was something. The Harrier GR.7 can carry Sidewinder, but has no ability to search for aircraft other than by MkI eyeball.
The decision was made because the MoD does not have the funds to upgrade two different Harrier fleets. Among other things, the Sea Harriers need a more powerful engine and the RAF Harriers need radar.
It may also have something to do with the decision to buy the F-35 (formerly JSF) for its new carriers. Eventually, they will be able to fulfill the fleet air defense mission nicely. Unfortunately, that time is at least a decade away.
As many of the Harrier pilots and crew as possible will be absorbed into the new joint Harrier force, although many of the RN pilots may resign rather than operate under RAF authority. The MoD plans to upgrade all the GR.7s to GR.9 standard, but this has not been defined, and there is no guarantee that it will include a radar.
The Future Carrier Borne Aircraft is dead, long live Future Joint Combat Aircraft (FJCA), which will be the F-35B Joint Strike Fighter.
The AIM-132 ASRAAM is now operational on the Tornado F.3, and Storm Shadow will be operational by the end of 2002.
USA
Both USS Kitty Hawk and USS Nimitz have been fitted with RAM. From May 1998 to June of 2001 during an overhaul, Nimitz was fitted with the Ship Self-Defense System, Mk2, and P&PB/S&SQ(21)2 Mk49 RAM launchers replacing the P&PB and S&SQ Phalanx. The SSDS is described in the article on page 15. Kitty Hawk was fitted with one RAM launcher in June - August of 2001 during a 3-month “Ship Restricted Availability” (a short refit, less extensive than an overhaul). She will also get a second launcher, although it is not known if it has been installed yet, or if SSDS was installed as well. The launcher replaced a NATO Sea Sparrow mount on the starboard bow.
On March 22nd, Kitty Hawk test-fired her RAM launcher successfully.
BT
Back to The Naval Sitrep #22 Table of Contents
Back to Naval Sitrep List of Issues
Back to MagWeb Master Magazine List
© Copyright 2002 by Larry Bond and Clash of Arms.
This article appears in MagWeb (Magazine Web) on the Internet World Wide Web.
Other military history and related articles are available at http://www.magweb.com