 The following scenario was designed for the Age of Battles miniature gaming system, produced by the Russian company - Zvezda. For more information on the Age of Battles gaming system and available products, check out my web site - www.gauntletinternational.com. I think you will be surprised by the quality and detail that the Russians have put into this effort. It was my good fortune to be in Moscow when Zvezda first made these products available and now I am able to make them available to you. Their support through continued scenario development and eventually an Age of Battles magazine shows long-term dedication to the hobby. Good luck on those morale rolls!
The following scenario was designed for the Age of Battles miniature gaming system, produced by the Russian company - Zvezda. For more information on the Age of Battles gaming system and available products, check out my web site - www.gauntletinternational.com. I think you will be surprised by the quality and detail that the Russians have put into this effort. It was my good fortune to be in Moscow when Zvezda first made these products available and now I am able to make them available to you. Their support through continued scenario development and eventually an Age of Battles magazine shows long-term dedication to the hobby. Good luck on those morale rolls!
HISTORY OF THE PELOPONNESIAN WAR
by Thucydides translated by Richard Crawley
The same winter the Ambraciots, as they had promised Eurylochus when they retained his army, marched out against Amphilochian Argos with three thousand heavy infantry, and invading the Argive territory occupied Olpae, a stronghold on a hill near the sea, which had been formerly fortified by the Acarnanians and used as the place of assizes for their nation, and which is about two miles and three-quarters from the city of Argos upon the sea-coast.
Meanwhile the Acarnanians went with a part of their forces to the relief of Argos, and with the rest encamped in Amphilochia at the place called Crenae, or the Wells, to watch for Eurylochus and his Peloponnesians, and to prevent their passing through and effecting their junction with the Ambraciots; while they also sent for Demosthenes, the commander of the Aetolian expedition, to be their leader, and for the twenty Athenian ships that were cruising off Peloponnese under the command of Aristotle, son of Timocrates, and Hierophon, son of Antimmestus.
On their part, the Ambraciots at Olpae sent a messenger to their own city, to beg them to come with their whole levy to their assistance, fearing that the army of Eurylochus might not be able to pass through the Acarnanians, and that they might themselves be obliged to fight single-handed, or be unable to retreat, if they wished it, without danger.
Meanwhile Eurylochus and his Peloponnesians, learning that the Ambraciots at Olpae had arrived, set out from Proschiurn with all haste to join them, and crossing the Achelous advanced through Acarnania, which they found deserted by its population, who had gone to the relief of Argos; keeping on their right the city of the Stratians and its garrison, and on their left the rest of Acarnania.
Traversing the territory of the Stratians, they advanced through Phytia, next, skirting Medeon. through Limnaea; after which they left Acarnania behind them and entered a friendly country, that of the Agracans. From thence they reached and crossed Mount Thymaus, which belongs to the Agraeans, and descended into the Argive territory after nightfall, and passing between the city of Argos and the Acarnanian posts at Crenae, joined the Ambraciots at Olpae.
Uniting here at daybreak, they sat down at the place called Metropolis, and encamped. Not long afterwards the Athenians in the twenty ships came into the Ambracian Gulf to support the Argives, with Demosthenes and two hundred Messenian heavy infantry, and sixty Athenian archers.
While the fleet off Olpae blockaded the hill from the sea, the Acarnanians and a few of the Amphilochians, most of whom were kept back by force by the Ambraciots, bad already arrived at Argos, and were preparing to give battle to the enemy, having chosen Demosthenes to command the whole of the allied army in concert with their own generals. Demosthenes led them near to Olpae and encamped, a great ravine separating the two armies. During five days they remained inactive; on the sixth both sides formed in order of battle.
The army of the Peloponnesians was the largest and outflanked their opponents; and Demosthenes fearing that his right might be surrounded, placed in ambush in a hollow way overgrown with bushes some four hundred heavy infantry and light troops, who were to rise up at the moment of the onset behind the projecting left wing of the enemy. and to take them in the rear.
When both sides were ready they joined battle; Demosthenes being on the right wing with the Messenians and a few Athenians, while the rest of the line was made up of the different divisions of the Acarnanians, and of the Arnphilochian carters. The Peloponnesians and Ambraciots were drawn up pell-mell together, vith the exception of the Mantineans, who were massed on the left, without however reaching , to the extremity of the wing, where Fury ochus and his men confronted the Messenians and Demosthenes.
The Peloponnesians were now well engaged and with their outflanking wing were upon the point of turning their enemy's right; when the Acarnanians from the ambuscade set upon them from behind, and broke them at the first attack, without their staying to resist, while the panic into which they fell caused the flight of most of their army, terrified beyond measure at seeing the division of Eurylochus and their best troops cut to pieces. Most of the work was done by Demosthenes and his Messenians, who were posted in this part of the field.
Meanwhile the Ambraciots ("ho are the best soldiers in those countries) and the troops upon the right wing, defeated the division opposed to them and pursued it to Argos. Returning from the pursuit, they found their main body defeated and hard pressed by the Acarnianians. with difficulty made good their passage to Olpae, suffering heavy loss on the way, as they dashed on without discipline or order, the Mantineans excepted, who kept their ranks best of any in the army during the retreat.
The battle did not end until the evening. The next day Menedaius, who on the death of Eurylochus and Macarius had succeeded to the sole command, being at a loss after so signal a defeat how to stay and sustain a siege, cut off as he was by land and by the Athenian fleet by sea, and equally so how to retreat in safety, opened a parley with Demosthenes and the Acarnanian generals for a truce and permission to retreat, and at the same time for the recovery of the dead.
The dead they gave back to him, and setting up a trophy took up their own also to the number of about three hundred. The retreat demanded they refused publicly to the army; but permission to depart without delay was secretly granted to the Mantineans and to Menedaius and the other commanders and principal men of the Peloponnesians by Demosthenes and his Acamanian colleagues; who desired to strip the Ambraciots and the mercenary host of foreigners of their supporters; and, above all, to discredit the Lacedaemonians and Peloponnesians with the Hellenes in those parts, as traitors and self-seekers.
While the enemy was taking up his dead and hastily burying them as he could, and those who obtained permission were secretly planning their retreat, word was brought to Demosthenes and the Acamanians that the Ambraciots from the city, in compliance with the first message from Olpac, were on the march with their whole levy through Amphilochia to join their countrymen at Olpae, knowing nothing of what had occurred.
Demosthenes prepared to march with his army against them, and meanwhile sent on at once a strong division to beset the roads and occupy the strong positions. In the meantime the Mantineans and others included in the agreement went out under the pretence of gathering herbs and firewood, and stole off by twos and threes, picking on the way the things which they professed to have come out for, until they had gone some distance from Olpae, when they quickened their pace.
The Ambraciots and such of the rest as had accompanied thern in larger parties, seeing them going on, pushed on in their turn, and began running in order to catch them up. The Acarnanians at first thought that all alike were departing without permission, and began to pursue the Peloponnesians; and believing that they were being betrayed, even threw a dart or two at some of their generals who tried to stop them and told them that leave had been given. Eventually, however, they let pass the Mantineans and Peloponnesians, and slew only the Ambraciots, there being much dispute and difficulty in distinguishing whether a man was an Ambraciot or a Peloponnesian. The number thus stain was about two hundred; the rest escaped into the bordering territory of Agraea, and found refuge with Salynthius, the friendly king of the Agraeans.
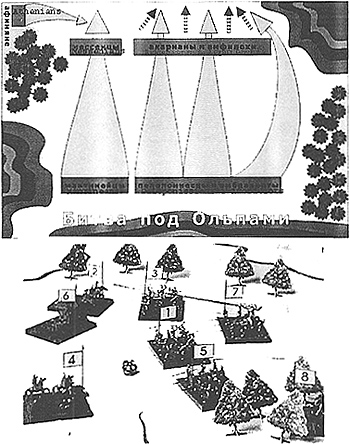
Scale
1 Figure=20 warriors.
Conditions of a victory
The first who destroys the Strategos of the enemy wins.
Peloponnessian Alliance
The left flank
- Mantineans
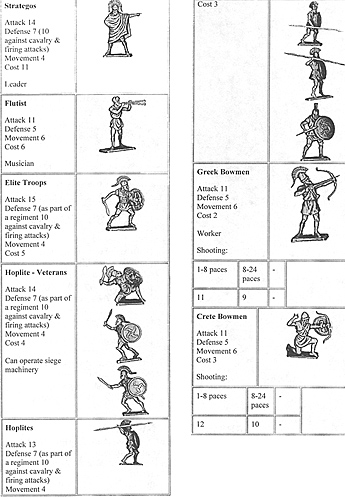
1 Strategist (Eurylochus)
5 Hoplite-veterans
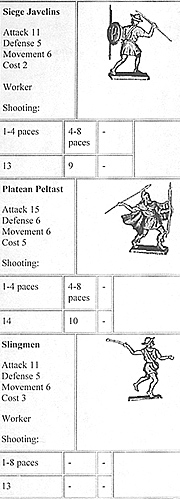
10 Javelin-men
The centre and the Right flank
- Peloponnesians
10 Hoplite-veterans
Ambraciots
20 Hoplite-civil guardsmen
25 Javelin-men
15 Sling-men
The Athenian Naval Union
Ambush
- Navpakt Messenians
5 Hoplite-civil guardsmen
15 Javelin-men
The right flank
- Athenians
1 Strategist (Dimosthenes, son of Alki
5 Hoplite-veterans
3 Bowmen
Navpakt Messenians
5 Hoplite-civil guardsmen
The centre
- Akarnanians
20 Hoplite-civil guardsmen
10 Javelin-men
10 Sling-men
The left flank
- Amphilochia
10 Javelin-men
| 
|
Back to MWAN #115 Table of Contents
Back to MWAN List of Issues
Back to MagWeb Magazine List
© Copyright 2002 Hal Thinglum
This article appears in MagWeb (Magazine Web) on the Internet World Wide Web.
Other military history articles and gaming articles are available at http://www.magweb.com